HANCI-Global
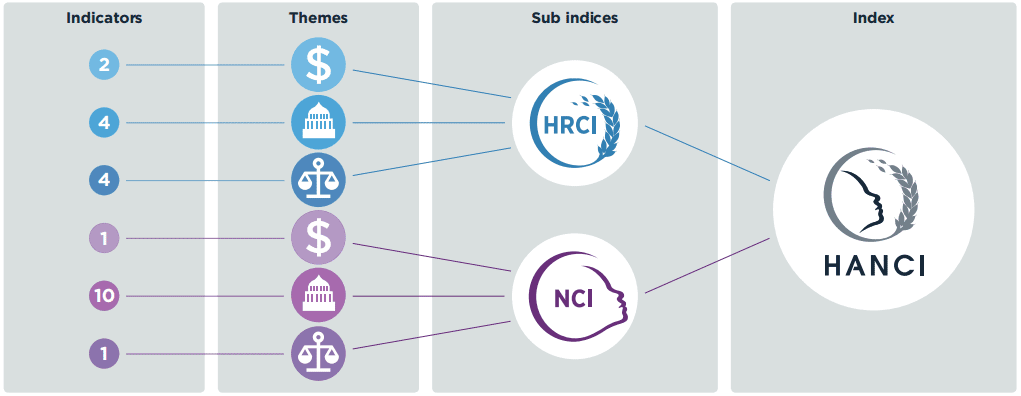
HANCI-Global compares and ranks the performance of 45 developing countries based on 22 indicators of political commitment. The indicators are split between indicators of commitment to hunger reduction (10 indicators) and indicators relating to commitment to addressing undernutrition (12 indicators). By separately analysing nutrition commitment and hunger reduction commitment we identify how governments prioritise action on hunger and/or undernutrition. We also show how diverse political commitment levels relate to levels of hunger and undernutrition. In both sets they are grouped under three themes:
- Laws (Legal frameworks - for example the level of constitutional protection of the right to food)
- Policies (government programmes and policies - for example the extent to which nutrition features in national development policies/strategies)
- Spending (public expenditures - for example the percentage of government budgets spent on agriculture)
This diagram shows the structure of the Index. Click on the themes to view the indicators.
Hunger Reduction Commitment Indicators - Public Spending
- 2014-2019government expenditures on agriculture as share of total government expenditures (Percentage)
Green if >=10
Yellow if <10 and >=7.5
Red if <7.5Source:IFPRI (SPEED database), ReSAKSS calculations using IMF Government Statistics and African Union
- 2017government expenditure on health as a share of total government expenditure (Percentage)
Green if >=15
Yellow if <15 and >=11.25
Red if <11.25Source:WHO Global Health Observatory Data Repository
Hunger Reduction Commitment Indicators - Policies
- 2005-2019Assesses the existence of an institutional, legal and market framework for secure land tenure and the procedure for land acquisition and accessibility to all.
The Ratings Scale goes from 6 (high) through 1 (low), as follows:
6 - Good for an 3 years
5 - Good
4 - Moderately Satisfactory
3 - Moderately Unsatisfactory
2 - Unsatisfactory
1 - Unsatisfactory for 3 years
Green if >=4
Yellow if between 2.99 AND 4
Red if <=2.99
Source:The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD) - 2004-2019This indicator assesses to what extent the agricultural research and extension system is accessible to poor farmers, including women farmers, and is responsive to the needs and priorities of the poor farmers. Coding is done in the same manner as for the ‘security of access to land’ indicator.
Green if >=4
Yellow if between 2.99 AND 4
Red if <=2.99
Source:The International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD)
- 2010-2019Percentage of children under five years of age who were registered at the moment of the survey.
Green if >=90
Yellow if between 70 AND 90
Red if <=70Source:UNICEF: DHS/MICS
- 2018-202010 = Social safety nets are comprehensive.
7 = Social safety nets are well developed, but do not cover all risks for all strata of the population.
4 = Social safety nets are rudimentary and cover only few risks for a limited number of beneficiaries.
1 = Social safety nets do not exist.
Green if >=7
Yellow if between 3 AND 6
Red if <=2
Source:Transformation Index of the Bertelsmann Stiftung (BTI)
Hunger Reduction Commitment Indicators - Laws
- 2014-2019Strong = 3 Explicit all citizens, specific groups or incorporated under living standards AND/OR Ratified international law (automatically assigned equal status as constitutional law)
Moderate = 2 Implicit as part of a broader right in constitutional law.
Weak = 1 Directive Principle (not justiceable) OR Likely or confirmed equality of ratified international lay to national legislation
Green if 3
Yellow if 2
Red if 1Source:FAO information paper and FAO web database on Right to Food (FAOLEX). - 2015-2019Score based on women’s legal rights and de facto rights to own and/or access agricultural land. Value based on the following scale:
1: Women and men have the same legal rights and secure access to land assets, without legal exceptions regarding some groups of women. Customary, religious and traditional laws or practices do not discriminate against women’s legal rights.
0.75: Women and men have the same legal rights and secure access to land assets, without legal exceptions regarding some groups of women. However, some customary, religious or traditional practices or laws discriminate against women’s legal right.
0.5: Women and men have the same legal rights and secure access to land assets. However, this does not apply to all groups of women.
0.25: Women and men have the same legal rights to own land assets; but not to use, make decisions and/or use land assets as collateral.
0: Women do not have the same legal rights as men to own land assets
(note: in HANCI calculation, the scoring used in the original source is reversed for consistency)
Green if 1
Yellow if 0.5
Red if 0Source:Social Institutions and Gender Index (SIGI) accessed via OECD’s Gender, Institutions and Development Database (GID-DB)
- 2019The extent to which women have equal economic rights in law and in practice. 0: there were no economic rights for women in law and systematic discrimination based on sex may have been built into law.
1: women had some economic rights under law, but these rights were not effectively enforced.
2: women had some economic rights under law, and the government effectively enforced these rights in practice while still allowing a low level of discrimination against women in economic matters.
3: all or nearly all of women’s economic rights were guaranteed by law and the government fully and vigorously enforces these laws in practice.
Green if 3
Yellow if 1 OR 2
Red if 0
Source:The Cingranelli-Richards (CIRI) Human Rights Data Project
- 1996-2019The Constitution clearly references a right to social security (see Annex II of the source document). 0= No; 1=Yes
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:FAO information paper and other sources
Nutrition Commitment Indicators - Public Spending
- 2017-20190 = no budgets or where no confirming information could be found; 0.5 = sectoral budgets for nutrition; 1 = separate budget line for nutrition
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:SUN Compendium of fiches; IDS Nutrition Governance; Save the Children Nutrition Barometer; WHO Landscape Analysis; Global Nutrition Report (N4G tracking tables).
Nutrition Commitment Indicators - Policies
- 1996-2018The percentage of children aged 6-59 months who received 2 high doses of vitamin A supplements within the last year.
Green if >=90
Yellow if between 70 AND 90
Red if <=70Source:MICS Indicators, UNICEF field offices and WHO, author calculations based on government data - 2010-2019Whether governments promote complementary feeding practices of children aged 6–9 months and continued breastfeeding of children at ages 12–15 and 20–23 months. 0 = no; 1= yes
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:Sun Reports; world breast feeding trends initiative - 2017-2019The percentage of population with access to an improved drinking-water source.
Green if >=90
Yellow if between 70 AND 90
Red if <=70Source:Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) for water supply and Sanitation - WHO/UNICEF - 2016-2019The percentage of population with access to improved sanitation facilities not shared with other households.
Green if >=90
Yellow if between 70 AND 90
Red if <=70Source:Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) for water supply and Sanitation - WHO/UNICEF - 2007-2019Percentage of women aged 15–49 years attended at least once during pregnancy by skilled health personnel (doctor, nurse or midwife)
Green if >=90
Yellow if between 70 AND 90
Red if <=70Source:UNICEF: DHS/MICS
- 2019The total count of key search terms in a selected policy document divided by the number of pages in the document. Search terms: nutritio*.*; undernutrition/under-nutrition; malnutrition/mal-nutrition nutrient; diet*.*; stunt*.*; wasting/wasted; short-for-age; short for age; height-for-age; height for age; weight-for-age; weight for age; weight for height; weight-for-height; Underweight; under-weight; Low birth weight; Thinness; Micro-nutrient; micronutrient; 1000 days; one thousand days; Breastfeed*.*; Behavior change; behaviour change; Iron deficiency anaemi/anemi; Zinc; Deworm; de-worm; Vitamin A; Supplementary feed; complementary feed.
Green if rank is >=31
Yellow if rank is 16 to 30
Red if rank is <=15Source:web-based searches.
- 2019Whether a national nutrition policy, plan or strategy exists. 1: Yes 0:No
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:EIU Global Food Security Index
- 2019Whether a multisectoral and multistakeholder coordination mechanism exists: 0 = no; 1 = yes
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:SUN fiches/Country docs and unpublished SUN country documents
- 2019Whether governments identify time bound nutrition targets in public policy documents: 0= no; 1 = yes
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:SUN Movement Annual Progress Reports; Global Nutrition Report
- 2005-2020Has there been a Demographic and Health Survey / Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey /comparable national nutrition survey in the past three years? 1: Yes if the survey was dated 2013 or thereafter, or currently underway. 0: No new survey undertaken after 2013.
Red if 0
Green if 1Source:UNICEF, DHS and national nutrition surveys
Nutrition Commitment Indicators - Laws
- 2019The extent to which the International Code for Marketing of Breastmilk Substitutes is enshrined in law.
4 = ICBMS is fully in law.
3 = Many provisions of ICBMS are in law.
2 = Few provisions are in law.
1 = No legal measures.
Green if 4
Yellow if 2 or 3
Red if 1
Source:‘Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes: National Implementation of the International Code, Status Report 2018.’
We include indicators that allow the index to assess ‘curative’ action (efforts that seek to address immediate needs) as well as ‘preventive’ action (efforts to avert hunger and undernutrition, to reduce food insecurity and to prevent people from becoming malnourished). Consequently, some of our proxy indicators measure interventions that are not primarily instituted to combat hunger or undernutrition (e.g. civil registration of births or investments in public health). Nevertheless, governments recognise that these efforts do contribute to hunger reduction and improved nutrition statuses in the short, medium and long term, and are therefore included in the index.
Donor Country Index
The donor country indicators looks at 23 OECD member countries and are compared based on 14 indicators which are split between indicators of commitment to hunger reduction (9 indicators) and indicators relating to commitment to addressing undernutrition (5 indicators). These are grouped under 2 themes:
- Policies, programmes and legal
- Public expenditures
You can read more about these on the Donor Index pages